Leisure and hospitality workers are quitting at the highest rates of any industry. About 1 million left the workforce in November 2021 alone, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Why? Seasonality, low pay and monotonous work are among the reasons for the hospitality industry’s churn rate, as well as a perceived lack of career advancement.
So what are hospitality businesses to do? Perhaps turn to services like Qwick, a startup that matches workers with hospitality gig contracts. Qwick today announced that it raised $40 million in a Series B financing round led by Tritium Partners, with participation by current investors Album VC, Kickstart, Desert Angels and Revolution’s Rise of the Rest Seed Fund.
Jamie Baxter co-founded Qwick in 2017 with Chris Loeffler. Baxter was previously the segment tech director of risk and financial services at Willis Towers Watson, where he oversaw product and software development.
With Qwick, Baxter sought to build a platform that connects service industry workers with food and beverage shifts in real time. Qwick uses a matching algorithm that takes into account factors like distance, the availability of “VIP” workers and supply to fill gigs for hospitality businesses, including stadiums, senior living facilities and corporate catering.
“The hospitality industry has been plagued with reputations of low retention rates, low wages and poor management and working conditions for decades,” Baxter told TechCrunch in an email interview. “Qwick aims to combat the issues of working in the industry and reshape what it means to work in hospitality by creating value for its professionals and offering them a livable wage.”
To sign up for Qwick, workers have to complete a profile and watch a five-minute virtual orientation. Once they’re vetted, they receive notifications for open shifts.
“Qwick requires incoming professionals to go through an orientation including a one-to-one interview,” Baxter said. “Before being granted access to the platform, all Qwick professionals have been certified and vetted for experience, professionalism and commitment to service.”
Baxter also says that Qwick utilizes a two-way, five-star rating system to “ensure continued quality and reliability between professionals and businesses,” although it bears noting that similar ratings systems on gig marketplaces have been found to exacerbate biases against minority workers,
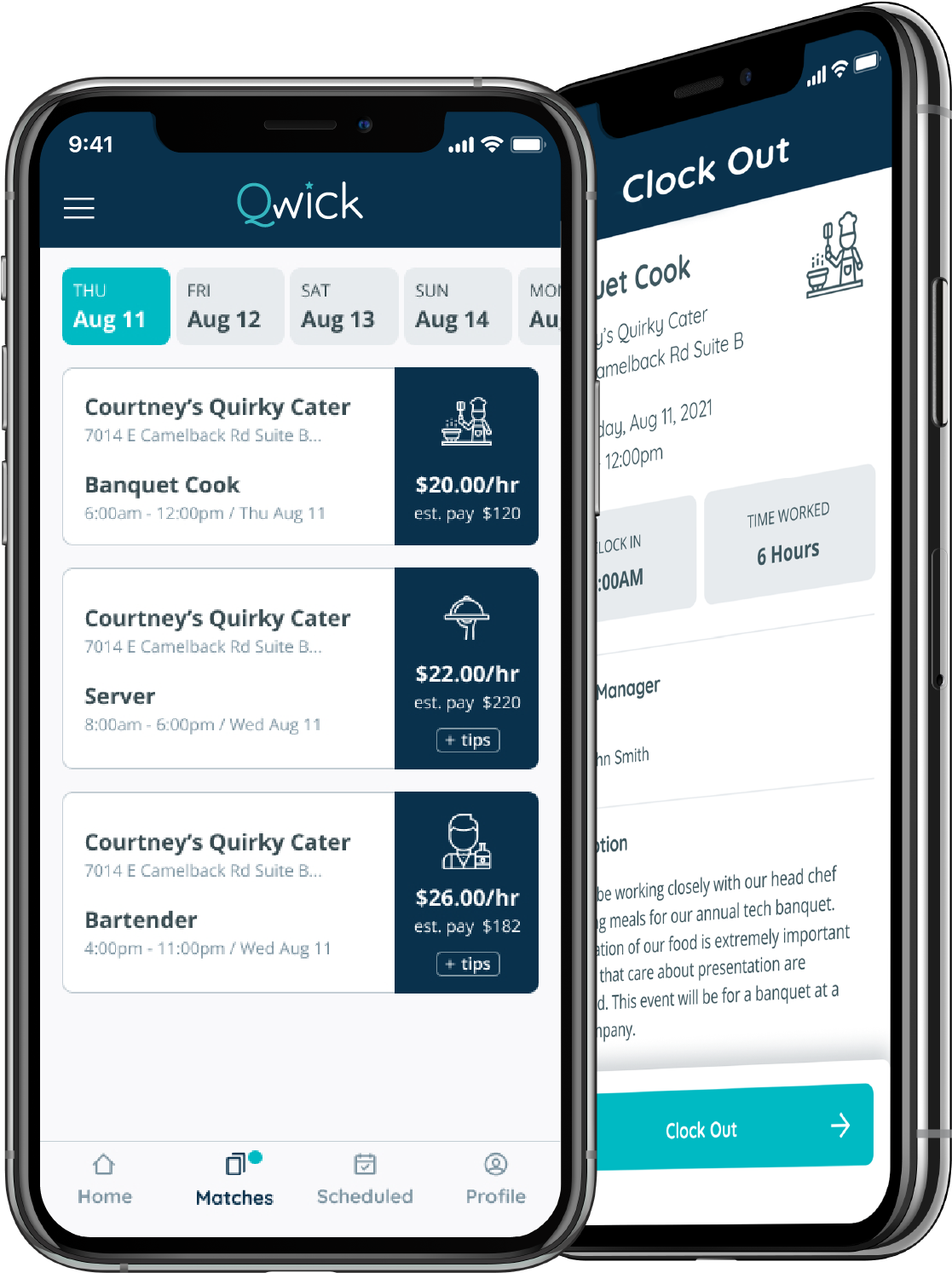
Booking gigs through Qwick’s mobile app. Image Credits: Qwick
Qwick is akin to startups like Stint, Flexy, Indeed Flex, Gig, Limber and Baristas on Tap, which provide short-term workers to businesses across a number of industries. Advocates for the platforms say that they’re making hospitality into a more financially viable profession by increasing job flexibility. But a recent Eater piece found that some workers on hospitality gig startups take home around the local minimum wage and might be forced to make lengthy unpaid commutes. Critics allege that the platforms could leave businesses with less budget for recruitment and training, encouraging them to replace full-time positions with temporary work.
Some hospitality employers have signaled they’re willing to embrace temp workers potentially at the expense of salaried employees. In 2017 and 2018, Marriott and Hilton joined with Airbnb and the TechNet coalition (which includes Uber, Lyft and Taskrabbit) to lobby for a federal bill that would classify anyone who finds work through an online platform as an independent contractor.
Baxter pushes back against the notion that Qwick is a force for ill, arguing it provides workers with the “freedom” to work on their schedules.
“Thousands of business partners across the U.S. rely on Qwick to end understaffing … [We] only partner with reputable businesses known to treat their staff well, and give professionals the agency to work where and when they want,” Baxter said. “Hundreds of thousands of industry professionals have downloaded our app and signed up to work shifts through Qwick.”
Qwick workers are paid an average of $9 above minimum wage in the cities where they work, Baxter added. He also noted that Qwick allows businesses to hire gig workers for traditional off-platform employment at no extra cost, unlike some gig work platforms that impose recruitment and hiring fees.
In any case, the demand for Qwick’s service seems very robust on the employer side. After a rough patch during the pandemic — Qwick was forced to lay off 70% of the team, and Baxter stopped taking a salary — business has more than recovered, with revenue having grown an astounding 10,000% over the past three years, according to Baxter.
And for better or worse, the gig economy shows no signs of contracting. The Pew Research Center reports that 16% of Americans have completed a job via an online gig platform. And Mastercard predicts that the number of global gig workers will rise to 78 million in 2023, up from 43 million in 2018.
Qwick is actively working with over 7,000 businesses across 23 metro areas, and the platform has facilitated over 500,000 shifts so far, Baxter added.
Qwick’s investors, for one, appear to be confident in Qwick’s long-term trajectory, whether or not it results in the best outcome for workers. In an emailed statement, Tritium Partners managing partner David Lack said: “Qwick’s impressive growth and history achieving success through its innovative hospitality solution, even through an especially challenging few years for the industry, indicate that the company has truly changed the way people work.”
To date, Arizona-based Qwick has raised $69.1 million in capital. The company has a staff of just over 270, which Baxter says will expand to around 300 before the end of the year.
Qwick raises VC money to match gig workers with hospitality jobs by Kyle Wiggers originally published on TechCrunch
DUOS





