Ghana’s Eastern neighbour, Togo spends $20 million every month to ensure the prices of essential goods are stable to protect consumers.
Amid the double whammy of Covid-19 and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Togo has been able to keep single digits with both headline and food inflation rates for September pegged at 7.90% and 8.60%, respectively.
According to Togo’s President, Faure Gnassingbe, who was speaking at the 2022 Qatar Economic Forum in Doha, the government is spending $20 million a month to cap prices of basic goods such as wheat, corn and fuel in their economy valued at $8.5 billion.
The President admitted, “That’s not sustainable for our finances so we are trying to set up a new strategy for the mid-and long-term.”
The West African nation is also taking steps to substitute essential imports and reduce emerging spending to curb inflation. For example, the state plans to urge bakers to mix wheat with locally-grown cassava to cut the import bill. At the same time, drivers of petrol-fueled motorbikes, the most widely used form of transportation, are also expected to switch to electric vehicles gradually.
Elsewhere in West Africa
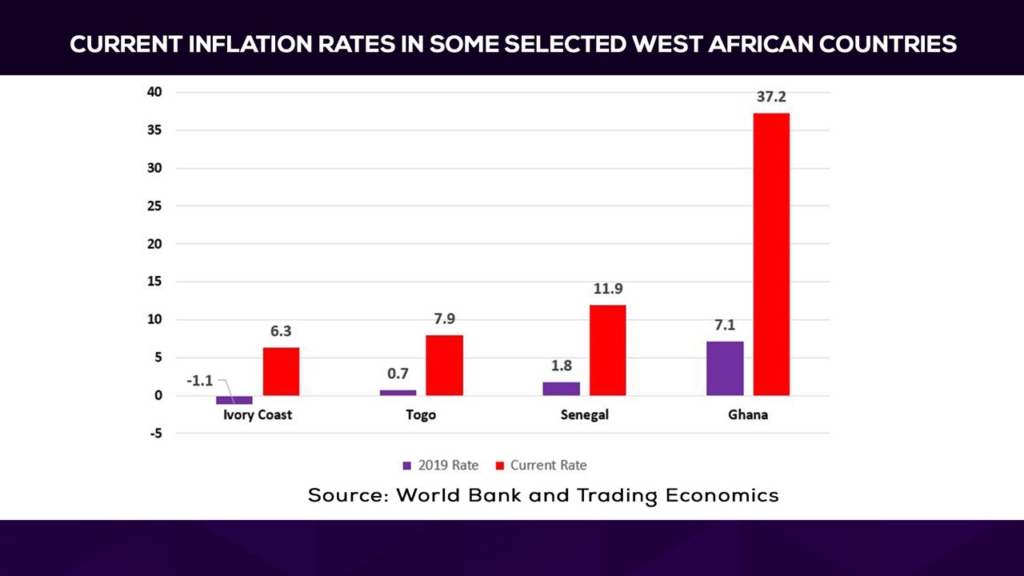
Although Togo’s headline inflation has gone up by more than tenfold, countries like Cote D’Ivoire have seen inflation move from a negative rate of 1.1% in 2019 to 6.3%. Senegal’s inflation rose from 1.8% in 2019 to the prevailing rate of 11.9%. In Ghana, inflation has skyrocketed from 7.1% [pre-Covid] to 37.2% for September 2022.
In his recent address to the nation, President Akufo-Addo admitted that “the whole world has been taken aback by the speed with which inflation has eaten away people’s incomes. Economies, big and small, have experienced, over this year alone, the highest rise in cost of living over a generation…”.
He emphasised that “between the end of 2019 and now, inflation in Ghana has increased by five-fold, in Togo by sixteen-fold, by eleven-fold in Senegal, and by seven-fold in Cote d’Ivoire.”





